Acid Reflux vs GERD Differences and How to Manage Them Effectively
When it comes to the differences between acid reflux and GERD and how to manage them, understanding the nuances is key. Acid reflux is sporadic and often manageable through lifestyle changes, while GERD is a chronic issue requiring more persistent treatment. This blog breaks down these conditions and offers management tips.
Key Takeaways
- Acid reflux is a temporary condition characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, while GERD is a chronic form of acid reflux occurring more than twice a week with more severe symptoms.
- Management strategies differ: occasional acid reflux can often be treated with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications, while GERD typically requires prescription medications and may involve surgical interventions.
- Untreated GERD can lead to serious complications, including esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus, which increases the risk of esophageal cancer, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and management.
Understanding Acid Reflux
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid moves back up into the esophagus, leading to a painful or burning sensation. This typically happens if the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring-like muscle serving as a gateway between your esophagus and stomach, relaxes inappropriately, permitting the backward flow of stomach contents. The LES may become weak or malfunction, which is when acid reflux ensues. To gain clarity on the causes and management and better understand acid reflux and GERD, it’s essential to explore their symptoms, triggers, and treatment options.
The symptoms often associated with acid reflux comprise a burning feeling within one’s chest region, commonly known as heartburn. There are other indicators, like experiencing an upward surge of gastric content into the esophagus that irritates its lining – this process is termed acid regurgitation. Those who routinely suffer from heartburn might notice these symptoms intensifying following the consumption of substantial meals or adopting horizontal positions shortly after eating. Such events should be taken into consideration in the discussion on acid reflux.
Crucially important in controlling instances of acid reflux is maintaining proper functioning of the LES by altering certain lifestyle practices—for instance, favoring smaller meal portions and avoiding foods that trigger discomfort can help reduce episodes linked to acid reflux. For immediate symptom alleviation during acute occurrences, antacids can neutralize excess gastric acids effectively, while H2 blockers aim at curtailing their production within your system for more sustained relief.
What is GERD?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition characterized by persistent acid reflux and is associated with digestive and kidney diseases. It’s typically identified when symptoms of acid reflux present themselves more than two times per week. Frequent episodes of gastroesophageal reflux can weaken the esophagus’ ability to contain stomach acids, allowing them to flow back into the esophagus more easily. The continuous assault from stomach acid may lead not only to discomfort but also to potential long-term issues, making GERD a pressing health matter for numerous individuals.
The signs of GERD are often far worse and regular compared to those experienced with occasional bouts of acid reflux. Persistent heartburn and challenges in swallowing are among the common symptoms noted, along with chest pain and a sour or bitter taste that persists in one’s mouth. These indicators can significantly impact an individual’s everyday life and overall well-being, frequently necessitating professional medical care.
For accurate confirmation of GERD diagnosis, medical practitioners might employ diagnostic methods, including barium X-ray or upper endoscopy examinations, that allow visualization within the esophagus while evaluating damage caused by acidic exposure. Detecting gastroesophageal reflux disease early plays a crucial role in effectively managing it before any serious complications arise.
Key Differences Between Acid Reflux and GERD
Acid reflux and GERD both result in the upward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, yet they are differentiated by how often and intensely symptoms present themselves. While occasional acid reflux happens sporadically due to certain dietary choices or behaviors, GERD manifests with more frequent (occurring more than twice weekly) and severe symptoms. Heartburn related to GERD tends to be stronger and longer-lasting compared to the less intense heartburn that accompanies episodic acid reflux.
The strategies for handling acid reflux versus those for managing GERD differ substantially. For dealing with infrequent bouts of acid reflux, lifestyle changes coupled with over-the-counter remedies usually provide relief. In contrast, addressing GERD might necessitate prescription medications or even surgical procedures aimed at alleviating persistent symptoms and forestalling Health issues. Recognizing these differences is crucial for applying appropriate treatment measures that can significantly enhance one’s well-being.
Common Symptoms of Acid Reflux and GERD
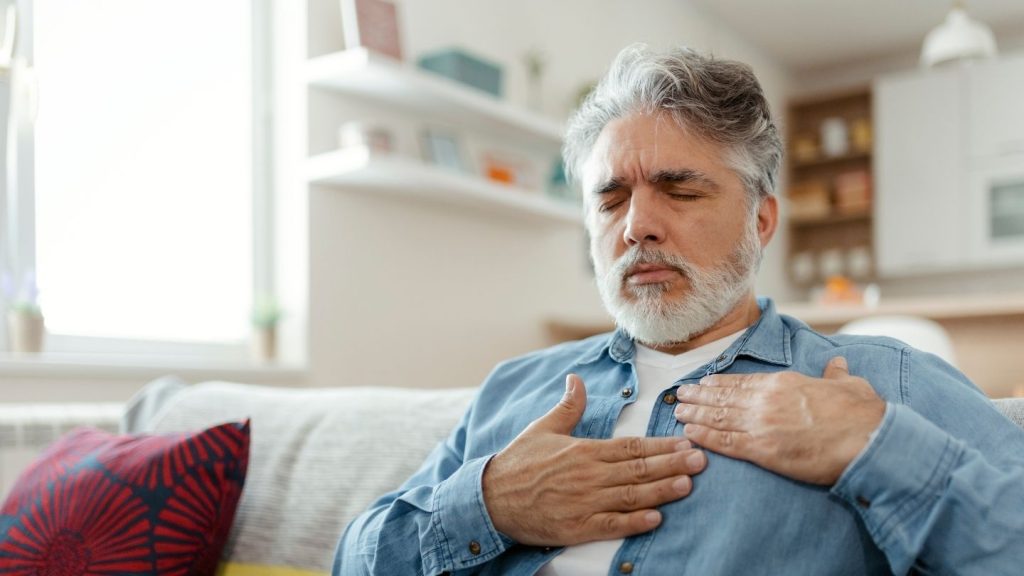

Acid reflux and GERD frequently lead to symptoms like chest pain, which is often accompanied by a burning sensation known as heartburn. This discomfort typically manifests after meals and is considered a defining feature of these digestive conditions. Understanding how to accurately convey the nature of heartburn includes recognizing its link with the mentioned symptoms.
There are other indications that may accompany acid reflux, such as the backflow of stomach contents or sour liquid, non-cardiac related chest discomfort, and feelings of nausea. Individuals could also endure swallowing difficulties, experience persistent coughing, or notice an acidic taste in their mouth. Correctly identifying this range of symptoms is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment strategies. Taking prompt measures can prevent acid reflux from developing into more severe GERD while averting Health issues.
Risk Factors and Causes
Numerous factors and causes can lead to the onset of acid reflux and GERD, including:
- A considerable risk factor is obesity, which heightens the probability of developing GERD.
- Lifestyle habits such as smoking or consuming high-fat foods may worsen the symptoms associated with GERD.
- Fatty foods are particularly known to elevate stomach acid production, resulting in more instances of acid reflux.
Medical conditions that slow gastric emptying might play a role in increasing susceptibility to GERD by raising stomach pressure. The bodily changes and added abdominal pressure during pregnancy also serve as a contributing risk factor for this condition. Certain medications, like aspirin, have been noted for their ability to weaken the lower esophageal sphincter, thus intensifying symptoms related to acid reflux.
Should GERD remain unchecked chronically, it significantly increases the risks connected with Barrett’s esophagus, an affliction characterized by abnormal cellular transformation within the esophagus. Being overweight or obese compounds these dangers due to increased strain on the abdominal regions, leading to exacerbated reflux issues. For individuals diagnosed with Barrett’s esophagus, periodic surveillance endoscopies become imperative tools for monitoring dysplasia levels while keeping vigilant against early indicators of cancer within the esophagus.
Complications of Untreated GERD
If not addressed, GERD can lead to severe consequences. Esophagitis is a prevalent outcome and involves inflammation of the esophagus due to consistent acid exposure. This condition may result in discomfort and create difficulty swallowing, which could degrade one’s quality of life.
A more alarming complication that can arise from untreated GERD is Barrett’s esophagus. In this condition, abnormal cells replace normal ones within the esophageal lining, thereby escalating the risk for developing a dangerous type of cancer known as esophageal adenocarcinoma. Individuals diagnosed with Barrett’s esophagus face a substantially increased threat of contracting this form of cancer compared to those without it. They encounter an approximate annual cancer risk between 0.1% and 0.3%.
It is crucial to identify and manage GERD promptly in order to prevent these serious complications from occurring.
Managing Occasional Acid Reflux
Addressing occasional acid reflux typically requires some adjustments to one’s lifestyle habits. Ceasing smoking can markedly enhance digestive health, and decreasing alcohol intake may lessen stomach acid production, thereby diminishing the likelihood of experiencing acid reflux episodes. Including foods such as bananas and oatmeal in your diet could calm the stomach and mitigate reflux symptoms.
To reduce stress on the lower esophageal sphincter, which stops it from loosening improperly, it is advisable to eat smaller meals more regularly throughout the day. For immediate symptom relief, over-the-counter remedies like antacids are effective in neutralizing excess stomach acid. Alternatively, H2 blockers can decrease stomach acid output. To avoid nighttime bouts of reflux that disrupt sleep quality, raising the head-end of your bed between six and eight inches during meals is beneficial.
Steering clear of known dietary triggers, including spicy culinary creations and specific acidic foods or beverages with carbonation, can also be instrumental in controlling symptoms associated with this condition. Identifying personal trigger items and avoiding them accordingly will substantially aid in lessening occurrences of these uncomfortable episodes related to acid reflux.
Treatment Options for Chronic GERD
Beyond simple lifestyle changes and readily accessible over-the-counter remedies, chronic GERD management can involve powerful prescription drugs. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), alongside other specific medications, stand out as some of the most potent treatments prescribed to control GERD by significantly decreasing the production of stomach acid and offering sustained symptom relief. These are particularly beneficial for individuals whose severe symptoms persist despite trying alternative therapies.
Emerging interventions such as the LINX device bring renewed optimism for those suffering from GERD. The mechanism employs a string of magnetic beads that act to restrain acid reflux yet still permit food passage through the esophagus, posing a less invasive choice relative to conventional surgical procedures while demonstrating encouraging outcomes in symptom mitigation and life quality enhancement.
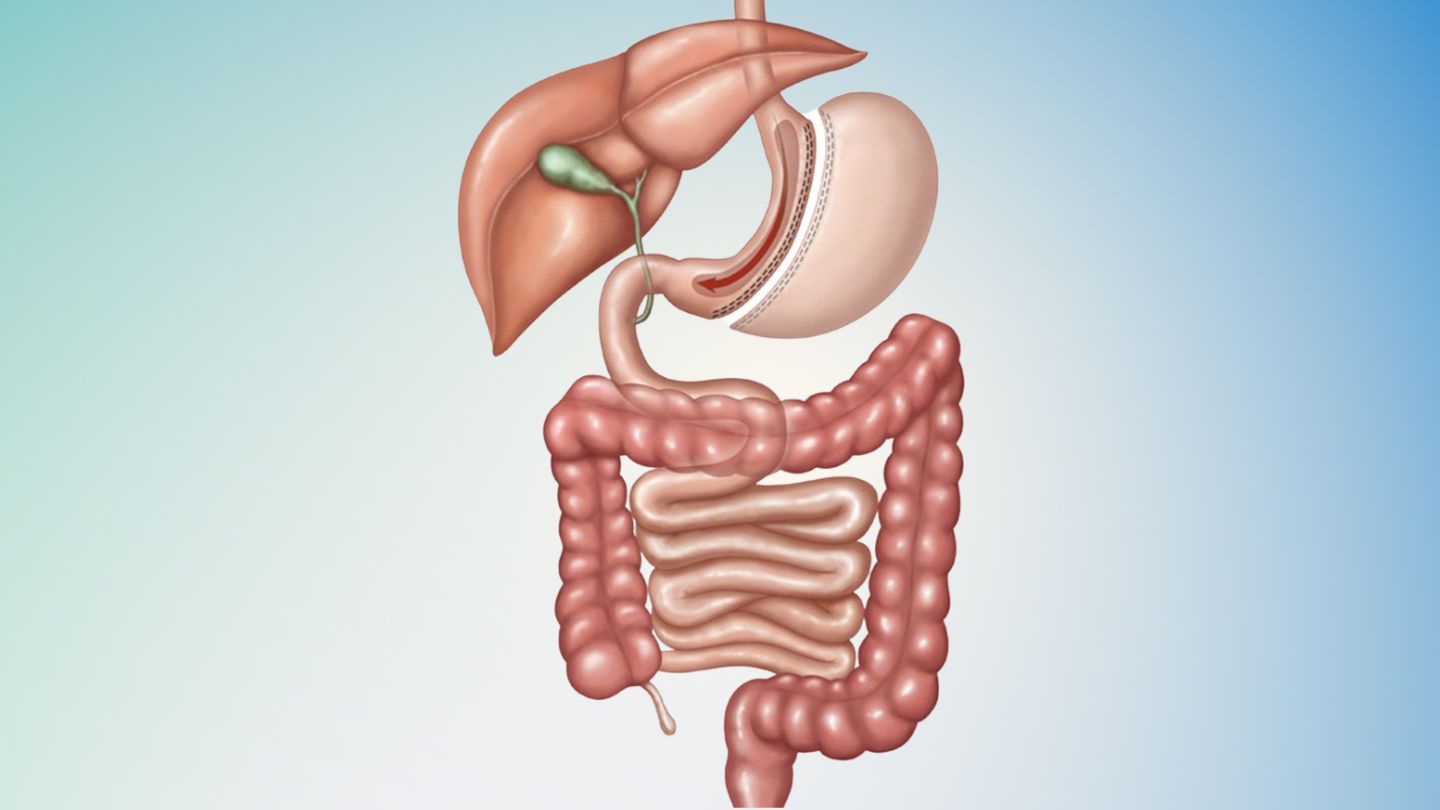
For more acute instances of both GERD and hiatal hernia, surgical strategies like laparoscopic fundoplication present viable alternatives. This minimally invasive approach encompasses encircling part of the upper stomach around the lower region of the esophagus with the aim of bolstering its closure capacity, hence obstructing acid reflux occurrences. Collectively, these medical solutions offer diverse approaches tailored toward efficacious long-term management of persistent GERD conditions.
When to See a Doctor
It’s crucial to recognize the appropriate time for seeking medical guidance when dealing with acid reflux and GERD. If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms that last more than two weeks, even after trying over-the-counter medications, it’s recommended to consult a doctor. Likewise, if heartburn continues despite undergoing treatment, this should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional.
Any alteration in the pattern or intensity of heartburn that interferes with sleep or daily routines calls for medical scrutiny. Symptoms such as unexplained weight loss or trouble swallowing necessitate immediate attention from a healthcare provider. Enduring nausea, vomiting, constant hoarseness of voice, wheezing, along with frequent bouts of heartburn, are signs that one should seek medical evaluation.
Preventive Measures
To stave off acid reflux and GERD, making adjustments to one’s lifestyle is essential. Achieving and sustaining a healthy weight can greatly diminish the likelihood of these conditions, while steering clear of certain foods known to provoke them, such as hot spices or citrus fruits, is key in controlling their symptoms.
Adopting additional strategies can also aid in preventing discomfort. This includes eating smaller meals more often to lessen the burden on the stomach, shunning snug attire, and remaining vertical for two to three hours post-mealtime. Exercises focused on diaphragmatic breathing could benefit some individuals by alleviating GERD-related symptoms.
Finding Relief and Long-Term Solutions
Understanding the key differences between acid reflux and GERD is crucial for taking control of your digestive health. While acid reflux is typically occasional and manageable with lifestyle changes, GERD is a chronic condition that can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Identifying the symptoms early and seeking the appropriate medical evaluation ensures better long-term outcomes and improves overall quality of life.
At Wellstar Comprehensive Bariatric Services, we provide advanced support and personalized care to help individuals overcome digestive issues like GERD. If you’re struggling with symptoms and need GERD acid reflux treatment in Marietta, Smyrna, Cobb, Austell, LaGrange, or West GA, our team is here to guide you toward effective, lasting relief through surgical and non-surgical options. Let us help you take the first step toward better health and a more comfortable life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between acid reflux and GERD?
Acid reflux is a temporary condition characterized by occasional backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, whereas GERD is a chronic condition marked by frequent and more severe symptoms.
What are the common symptoms of GERD?
Common symptoms of GERD include persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and a sour or bitter taste in the mouth.
It is important to seek medical advice if these symptoms occur frequently.
When should I see a doctor for acid reflux?
You should see a doctor for acid reflux if symptoms persist for more than two weeks, if over-the-counter medications fail to provide relief, or if you experience unexplained weight loss or difficulty swallowing.
Prompt medical attention is essential in these cases.
What lifestyle changes can help manage acid reflux?
Making alterations in your daily habits, like stopping smoking, decreasing the amount of alcohol you drink, eating less sizable meals, and avoiding foods that provoke symptoms, can successfully control acid reflux.
Such transformations have the potential to greatly improve both your comfort levels and general health.
What treatment options are available for chronic GERD?
The treatment options for chronic GERD encompass proton pump inhibitors, the LINX device, and surgical interventions such as laparoscopic fundoplication.
It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable option for individual conditions.