Understanding Your Options: Lipo vs Gastric Bypass
Body contouring and weight loss procedures are often discussed together, but they serve very different purposes. Some treatments focus on removing localized fat, while others are designed to treat obesity and related health conditions. Understanding how each option works, who it’s best suited for, and what results to expect is essential before making a decision. Your overall health, weight goals, and long-term expectations should guide the path you choose. In this blog, we’ll break down the key differences between liposuction and gastric bypass, including benefits, limitations, recovery, and which option may align best with your goals.
Key Takeaways
- Gastric bypass is a medically necessary weight loss surgery designed for significant, long-term weight reduction and health improvement, while liposuction is a cosmetic procedure focused on removing small, localized fat deposits for body contouring.
- For individuals with a body mass index of 35 or higher, or those living with obesity related health conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea, gastric bypass is generally the more effective and appropriate choice.
- Liposuction does not treat obesity, does not meaningfully improve metabolic health, and typically results in only a few pounds of weight change, it offers no direct benefits for longevity or disease resolution.
- Gastric bypass requires lifelong commitment to nutrition, supplementation, and lifestyle changes, but it can dramatically reduce health risks, resolve chronic conditions, and decrease medication needs.
- Speaking with a board-certified bariatric surgeon is the best first step for anyone with a BMI of 35–40 or higher, especially if obesity has persisted for years despite diet and exercise efforts.
Lipo vs Gastric Bypass at a Glance
When years of diet and exercise alone haven’t produced the lasting results you need, it’s natural to explore other options. For many adults across the United States and around the world, the conversation eventually turns to surgery, and two procedures often come up in the same breath: liposuction and gastric bypass. While both involve fat and body weight, they serve very different purposes and are designed for very different individuals.
Gastric bypass surgery is a weight loss surgery, a medically necessary bariatric procedure that restructures your digestive system to help you lose weight and improve serious health conditions. Liposuction, on the other hand, is a cosmetic procedure that removes excess fat from specific areas to refine your body’s shape. One addresses the root causes of obesity; the other sculpts the surface.
This blog is here to help you quickly understand which option aligns with your weight, your health status, and your long-term goals. If you’ve been living with a body mass index of 35 to 40 or higher, or if you’ve struggled with obesity related conditions for years, the evidence strongly supports gastric bypass as the path to meaningful, sustainable change. For those already near their ideal weight who simply want to smooth stubborn fat pockets, liposuction may have a role. Let’s explore the key differences so you can make an informed, confident decision.
What Is Liposuction?
Liposuction is a cosmetic surgery that uses small incisions and suction to remove localized fat deposits from targeted areas of the body. Common treatment zones include the abdomen, thighs, hips, arms, back, and under the chin. The goal is to refine and smooth body contours, not to produce major weight loss.
Typical candidates for liposuction include:
- Adults close to their ideal weight (generally a BMI under 30)
- Individuals with good skin elasticity can expect smooth results
- Those with realistic expectations about outcomes
- People without uncontrolled medical conditions
During the procedure, a surgeon injects a tumescent solution (containing saline, lidocaine, and epinephrine) into the treatment area to minimize bleeding and discomfort. A thin tube called a cannula is then inserted through small incisions to suction out fat cells. Recovery typically involves 1–2 weeks of downtime and wearing compression garments to support healing.
Common reasons people choose liposuction:
- Smoothing stubborn bulges that resist diet and exercise
- Improving how clothes fit
- Refining body shape after pregnancy or previous weight loss
- Treating small areas like a double chin or love handles
It’s important to understand that liposuction removes excess fat in limited amounts, usually just a few pounds. This medical procedure does not qualify as treatment for obesity and does not produce the significant weight loss needed by those who are significantly overweight.
What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
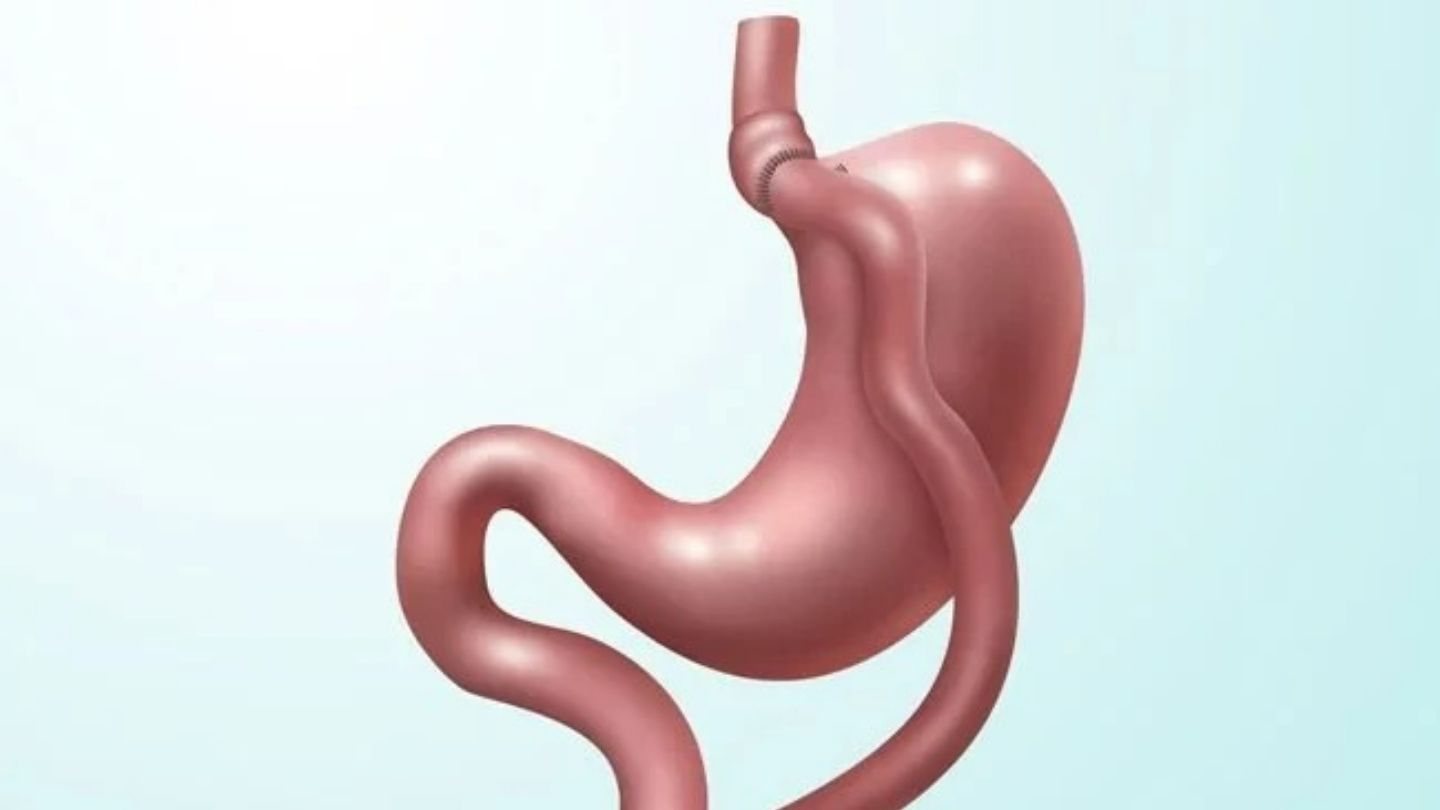
Gastric bypass surgery, specifically the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a bariatric surgery designed to help patients lose weight substantially and durably, and understanding revision possibilities is important when asking whether you can get gastric bypass twice. The surgeon creates a small stomach pouch about the size of an egg, capable of holding roughly one ounce of food compared to the stomach’s typical capacity of several cups. The small intestine is then rerouted to connect directly to this pouch, bypassing a large portion of the stomach and the first section of the intestine.
Typical eligibility criteria for gastric bypass include:
- BMI of 40 or higher
- BMI of 35–39.9 with serious obesity related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, severe sleep apnea, heart disease, or uncontrolled high blood pressure
- A documented history of unsuccessful attempts to lose weight through diet and exercise
What makes gastric bypass so effective is how it changes your digestive tract and hormonal balance. By bypassing much of the stomach, the procedure reduces production of ghrelin, the hormone that triggers hunger, while increasing hormones like GLP-1 and PYY that promote fullness and improve insulin sensitivity. These metabolic shifts help many patients feel satisfied with smaller portions and experience fewer calories absorbed from the food they do eat.
Documented outcomes of gastric bypass include:
- Average excess weight loss of 60–80% within 12–24 months
- Up to 80–90% remission rates for type 2 diabetes, often within days to weeks
- 50–70% resolution of hypertension
- Significant improvements in sleep apnea, joint pain, and cardiovascular risk factors
This is not a cosmetic procedure, it is a life-saving weight loss procedure for many patients living with severe obesity. The health benefits extend far beyond the number on the scale.
Lipo vs Gastric Bypass: Core Differences
When comparing bariatric surgery to liposuction, the distinctions become clear quickly. These two procedures address fundamentally different problems and serve different populations.
Goals and Purpose
- Gastric bypass targets substantial, sustained weight loss and resolution of obesity related diseases
- Liposuction focuses on body contouring and removing stubborn fat from specific zones
Impact on Health
- Gastric bypass can improve or resolve type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea, and reduce long-term cardiovascular risk
- Liposuction offers no proven metabolic health benefits and does not affect blood sugar, blood pressure, or life expectancy
Typical Candidates
| Factor | Gastric Bypass | Liposuction |
| BMI Range | 35–40+ | Under 30 |
| Obesity-Related Diseases | Often present (diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea) | None or well-controlled |
| Weight Struggle Duration | Years of failed diets | Stable weight, near goal |
| Primary Goal | Health transformation and weight loss | Cosmetic refinement |
Expected Weight Loss

- Gastric bypass: 60–80% of excess weight (often 100+ pounds)
- Liposuction: Minimal scale change (typically 5–10 pounds maximum)
For anyone living with medically defined obesity, gastric bypass is generally the more appropriate, and more beneficial, option. Liposuction simply cannot address the root causes of excess body weight or improve health outcomes in the same meaningful way.
Quick Results vs Sustainable Weight Loss
One of the appeals of liposuction is the promise of quick, visible results. Within a few weeks of recovery, patients can see smoother contours in treated areas, a tempting proposition, especially before a special event or after pregnancy. However, these changes are purely cosmetic. The underlying weight problems, metabolic issues, and health risks remain unchanged.
Gastric bypass takes a different approach. Weight loss begins immediately after surgery, with many patients noticing significant changes within the first 4–6 weeks. The most dramatic results typically occur over the first 6–12 months, followed by slower, steady progress for up to 18–24 months. This gradual timeline reflects the body’s adjustment to new eating patterns, hormonal changes, and metabolic recalibration.
What does sustainable weight loss look like after gastric bypass?
- Many patients maintain 50–70% of their lost excess weight even 10+ years after surgery
- Long-term success requires adherence to dietary guidelines, regular exercise, and follow-up care
- The procedure enforces portion control physiologically, supporting lasting change
While liposuction vs gastric bypass may seem like a choice between fast cosmetic results and slower medical transformation, the truth is that only gastric bypass offers durable, meaningful change for those struggling with obesity. Quick wins from liposuction often disappoint long-term, as remaining fat cells can expand or new fat can accumulate in other areas without lifestyle improvement.
Health Benefits of Gastric Bypass vs Liposuction
This is where gastric bypass truly stands apart. If your goal is improving your overall health, not just your appearance, bariatric procedures like gastric bypass offer transformative benefits that liposuction simply cannot match.
Key health benefits of gastric bypass include:
- Type 2 diabetes: Up to 80–90% of patients experience remission, often within days to weeks after surgery, even before major weight loss occurs
- Blood pressure: 50–70% of patients see resolution of high blood pressure
- Sleep apnea: 80% or more experience significant improvement or complete resolution
- Joint pain: Reduced load on knees, hips, and back leads to improved mobility and comfort
- Cardiovascular risk: Lower rates of heart attack, stroke, and dyslipidemia over the long term
- Overall mortality: Studies show 30–50% lower all-cause mortality over a decade among gastric bypass patients compared to those who remain untreated
These health outcomes reflect real, measurable changes, not just improvements in self-esteem or how you look in photos, while long-term bariatric care also includes recognizing common digestive issues after the duodenal switch and how to manage them when discussing advanced procedures.
Liposuction, by contrast, can boost confidence and help with body image. It removes fat deposits in targeted zones. But it does not meaningfully change blood sugar levels, blood pressure readings, or long-term cardiovascular risk. For patients with serious obesity related diseases, choosing gastric bypass over liposuction can directly impact life expectancy and daily quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes and Maintenance After Each Procedure

Both surgeries require some degree of ongoing lifestyle responsibility, but the depth and importance of those changes are much greater after gastric bypass.
After Gastric Bypass:
- Structured post-operative diet progressing from liquids to soft foods to regular meals
- Focus on lean protein, vegetables, and portion control
- Lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation (B12, iron, calcium, and others)
- Regular follow-up visits with your bariatric team
- Commitment to regular exercise and physical activity
- Emotional support and behavioral health resources as needed
Structured post-operative diet progressing from liquids to soft foods to regular meals reflects principles similar to best practices for diet after duodenal switch surgery, where nutritional precision plays a critical role. Patients who undergo gastric bypass typically work with a multidisciplinary team, including surgeons, dietitians, nurses, and behavioral health clinicians, all focused on sustained weight loss and long-term well-being. This team-based approach supports both physical and mental health throughout the journey.
After Liposuction:
- Maintaining results requires a healthy lifestyle, including balanced eating and exercise
- No metabolic or hormonal changes occur, so discipline relies entirely on personal habits
- Weight gain can still occur, and fat may redistribute to untreated areas if caloric intake exceeds output
For individuals ready to embrace permanent lifestyle changes to protect their health, gastric bypass offers a more powerful, medically supported “reset” than liposuction ever could.
When Liposuction Might Be the Right Choice
While this guide favors gastric bypass for obesity treatment, there are specific situations where liposuction is appropriate and useful.
Ideal candidates for liposuction include:
- Individuals within about 20–30 pounds of their goal weight
- Those with a stable weight for at least 6–12 months
- People looking to refine specific areas like love handles, lower belly, saddlebags, or a double chin
- Patients with good skin elasticity and realistic expectations
A particularly common scenario: patients who have already achieved long-term weight loss through gastric bypass or gastric sleeve surgery and now want to remove small, resistant fat pockets to complete their transformation. In this case, liposuction serves as a finishing touch rather than a primary weight loss solution.
When liposuction is not recommended:
- BMI of 35–40 or higher
- Active obesity related conditions like uncontrolled diabetes or hypertension
- Primary goal is to lose weight or improve health issues
- No prior attempt at bariatric surgery or medically supervised weight loss
Even when liposuction is the right cosmetic choice, it should complement, not replace, a healthy lifestyle.
When Gastric Bypass Is the Better Option
For individuals living with clinically significant obesity and long-standing health problems, gastric bypass is almost always the more appropriate choice.
Typical patient profiles for gastric bypass:
- BMI ≥40 (approximately 100 or more pounds over healthy weight)
- BMI ≥35 with type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, fatty liver disease, severe sleep apnea, PCOS, or joint degeneration limiting mobility
- History of years of failed diets, repeated weight cycling, and unsuccessful attempts at sustained weight loss with medications or commercial programs
- Significantly reduced quality of life due to weight and related conditions
For these individuals, focusing on cosmetic fat removal with liposuction fails to address the root cause and does nothing to reduce serious health risks. Liposuction is a cosmetic procedure, it cannot treat obesity or resolve the medical conditions that come with it. Medications or commercial programs may also lead patients to explore revisional considerations, such as whether you can get gastric bypass twice, exploring the possibilities in complex cases.
Another practical consideration: gastric bypass is often covered by insurance when medical criteria are met, because it is recognized as treatment for obesity and related diseases. Liposuction is typically self-pay because it’s categorized as elective and cosmetic.
Making the Right Decision for Your Health
Ultimately, this decision comes down to your health goals, not just how you want to look, but how you want to live. If you’re struggling with obesity related conditions like diabetes, sleep apnea, high blood pressure, or joint pain, gastric bypass or another bariatric option deserves careful consideration over liposuction.
Suggested next steps:
- Schedule a consultation with a board-certified bariatric surgeon
- Get a current BMI calculation and basic laboratory work
- Prepare a summary of your medical history and past weight-loss attempts
- Discuss both surgical and non-surgical options with your care team
While liposuction has a role in fine-tuning body shape for those already near their healthy weight, gastric bypass is usually the superior option when the main problem is obesity, not just isolated stubborn fat. This is a medically supported path that can resolve conditions, reduce medications, and extend your life.
Seeking a solution like gastric bypass is an investment in your future health, mobility, and quality of life. You deserve a team that sees the whole picture and helps you build a healthier future.
Choosing the Path That Fits Your Health Goals
Deciding between liposuction and bariatric surgery depends on your overall health, weight history, and long-term goals. While liposuction refines specific areas, gastric bypass addresses obesity and related medical conditions at their root. Understanding these differences helps you choose a treatment that supports lasting results, improved health, and realistic expectations.
At Wellstar Comprehensive Bariatric Services, we offer comprehensive evaluation and guidance for patients considering gastric bypass in Cobb County, Marietta, Smyrna, Austell, LaGrange, and West GA, helping us determine whether surgical weight loss is the right step. We also provide gastric sleeve, duodenal switch with gastric sleeve, revisional bariatric surgery, and treatment for GERD across Cobb County and surrounding communities. Connect with us today to explore a personalized plan designed to support meaningful, long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I have liposuction and gastric bypass, and if so, in what order?
For patients with obesity, gastric bypass or another bariatric procedure should come first to address overall weight and health conditions. Liposuction is typically considered 12–18 months later, once weight stabilizes and only small, resistant fat areas remain.
How long after a gastric bypass will I start to see major weight loss?
Many patients notice visible weight loss within four to six weeks. The most rapid changes usually occur during the first six to nine months, with slower, continued progress up to 18–24 months before stabilization.
Will my insurance cover gastric bypass but not liposuction?
Insurance commonly covers gastric bypass when medical criteria for obesity treatment are met. Liposuction is generally considered cosmetic and is usually not covered. Coverage varies by plan, so confirm benefits and authorization requirements directly with your provider.
What happens if I regain weight after a gastric bypass?
Some weight regain is common over time, but most patients maintain significant overall loss. Early follow-up, nutrition counseling, and behavioral support help address regain. In certain cases, medications or revisional procedures may be considered.
Is there a non-surgical alternative that gives results similar to gastric bypass?
Lifestyle programs and newer weight-loss medications can produce meaningful results, but typically do not match the long-term durability of gastric bypass. These options may benefit selected patients, particularly those not ready or eligible for surgery.