
Understanding Dumping Syndrome After Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Dumping syndrome after gastric sleeve surgery, called rapid gastric emptying, happens when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, leading to symptoms like bloating and diarrhea. This blog will explain what dumping syndrome is, why it occurs after gastric sleeve surgery, and ways to manage it.
Key Takeaways
- Dumping syndrome affects 20% to 50% of gastric surgery patients, causing rapid gastric emptying and symptoms like fainting, but these are rarely permanent.
- Dietary management, including avoiding high-sugar foods and consuming smaller, protein-rich meals, is essential to alleviate symptoms of dumping syndrome.
- Long-term management requires lifelong dietary adjustments, regular medical support, and lifestyle changes, including adequate fluid and protein intake, to maintain health post-surgery.
What Is Dumping Syndrome?
Dumping syndrome, also known as rapid gastric emptying, refers to a set of symptoms resulting from the quick passage of stomach contents into the small intestine. This condition frequently occurs in individuals who have had gastric surgeries like sleeve gastrectomy or especially gastric bypass, with an estimated 20% to 50% affected and up to 85% of gastric bypass patients experiencing it at different levels.
The issue arises when undigested food swiftly moves into the small intestine from what is usually a smaller stomach pouch created during surgery due largely to the premature opening of the pyloric valve. The consequent abrupt transition can cause discomfort ranging from mild symptoms to more intense reactions. Although dumping syndrome doesn’t pose severe health risks or become life-threatening, it can considerably impede daily living if not managed effectively. Most people suffering from this condition typically see an improvement over time, and in many cases, it’s not long-lasting.
Comprehending how dumping syndrome functions is crucial for those about to undergo or who have undergone any form of gastric operation so that they are able to better manage their post-operative lifestyle adjustments accordingly.
Causes of Dumping Syndrome After Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Dumping syndrome after gastric sleeve surgery is fundamentally caused by the swift movement of food from the stomach into the small intestine, a phenomenon known as rapid gastric emptying. The modification in size and function of the stomach due to surgery prompts this accelerated transit. As a result, patients may experience an array of distressing symptoms linked to this faster digestive process.
Early dumping syndrome can be aggravated when consuming refined sugars or high-glycemic-index carbohydrates. These substances cause a surge in intestinal fluid volume and content, which stimulates early dumping symptoms such as bloating and diarrhea through abrupt shifts in fluids and gut hormone secretion that accompany digestion. Healthcare providers diagnose dumping syndrome based on patient-reported symptoms and their timing, often using tests like a glucose tolerance test or hydrogen breath test to assist in making an accurate diagnosis.
Understanding these triggers allows individuals who have undergone gastric sleeve surgery to better manage dumping syndrome by making appropriate dietary modifications, thus enhancing their quality of life post-surgery.
Types of Dumping Syndrome: Early Dumping Syndrome and Late Dumping Syndrome
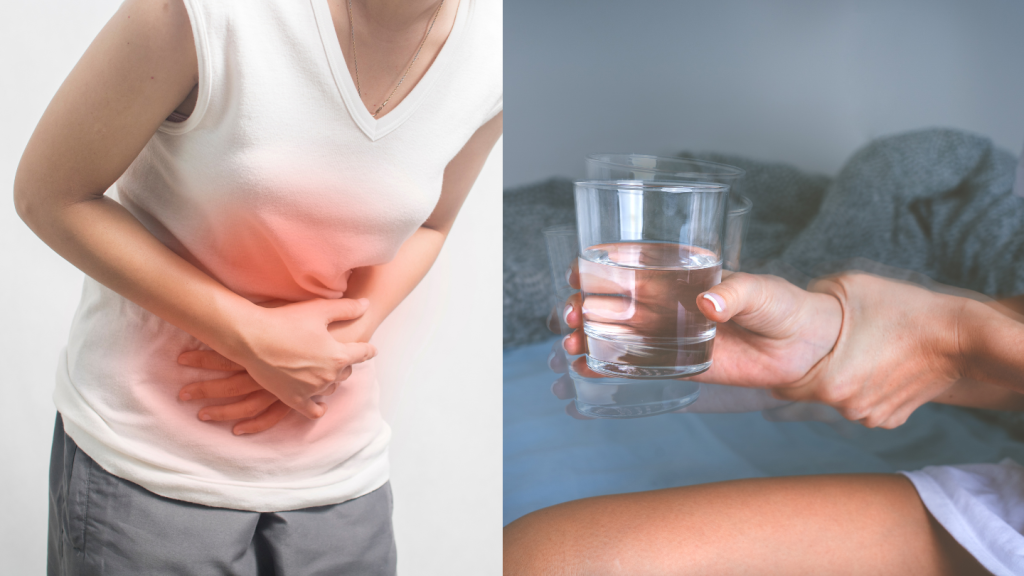
Early dumping syndrome typically occurs within 10 to 30 minutes after eating when undigested food rapidly moves into the small intestine. This can lead to symptoms like bloating, sweating, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea due to sudden fluid shifts and hormone release. Recognizing these early signs is key to managing the condition with appropriate dietary changes.
Late dumping syndrome arises 1 to 3 hours post-meal, often due to reactive hypoglycemia following high carbohydrate intake. This results in symptoms such as weakness, confusion, and tremors. Understanding these late symptoms helps in making dietary adjustments, like reducing refined sugars, to prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
Symptoms of Dumping Syndrome
Dumping syndrome manifests shortly after eating, with typical early dumping symptoms comprising bloating, sweating, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. These symptoms tend to emerge within 30 to 60 minutes following food consumption due to the rapid transit of ingested substances into the small intestine, leading to abrupt changes in fluid distribution throughout the body. Additionally, fluctuations in blood pressure can occur, causing symptoms such as lightheadedness or fainting.
The common indicators of early dumping include:
- Bloating
- Sweating
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea
Such symptoms arise as a direct consequence of food’s hasty progression into the intestines, which prompts an immediate alteration in bodily fluids balance.
Several hours after meals, late dumping syndrome can occur and is characterized by swift fluctuations in blood sugar levels. During these incidents involving low blood sugar or hypoglycemia, individuals might experience weakness, possibly leading to fainting episodes along with sensations of discomfort, indicating potential trouble ahead.
Recognizing these patterns permits those affected by dumping syndrome to both early and late manifestations to preventively manage their condition better. Pinpointing when such signs appear alongside understanding their specific nature enables proactive response, including lifestyle or dietary adjustments aimed at alleviating aspects associated with this disorder.
Diagnosing Dumping Syndrome
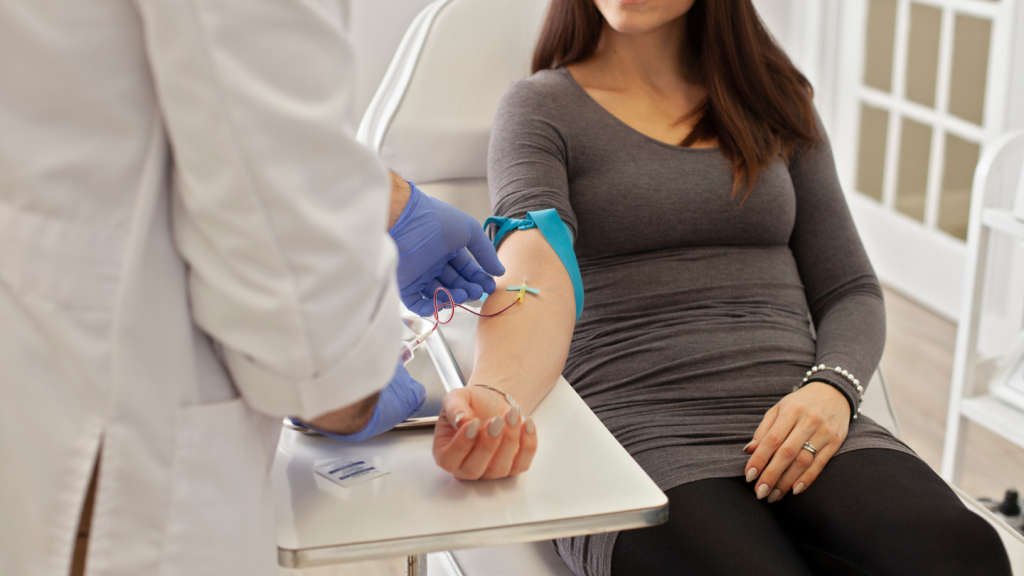
To diagnose dumping syndrome based on the symptoms and timing reported by patients, especially after gastric bypass surgery, healthcare practitioners utilize various tests. The glucose tolerance test is common. It requires patients not to eat for at least ten hours before ingesting a sweetened solution, with subsequent blood draws tracking bodily responses. If there’s a notable elevation in both heart rate and hematocrit levels following sugar intake, it could point toward dumping syndrome.
The hydrogen breath test also serves as an effective diagnostic measure by assessing how quickly food moves through the digestive system based on hydrogen levels detected in the breath after eating foods high in complex carbohydrates. Medical professionals may employ a gastric emptying scan that uses radioactive substances to monitor how quickly food exits from the stomach.
Healthcare providers rely on these diagnostic instruments alongside comprehensive symptom evaluations to ensure accurate identification of dumping syndrome diagnosed after gastric bypass surgery, thereby facilitating the development of customized treatment strategies for their patients.
Managing Dumping Syndrome Through Diet
Managing dumping syndrome effectively requires dietary adjustments. To mitigate the risk of symptom onset, it is important to minimize intake of foods rich in sugars and starches. Steering clear of simple carbohydrates found in items like white flour or table sugar is crucial. Drinking fluids during meals can exacerbate symptoms. Thus, it’s recommended to wait at least 30 minutes post-meal before having any liquids. Gastric bypass surgery-treated patients often need to follow these dietary strategies to manage their symptoms effectively.
To better control symptoms, distributing daily calorie consumption across six smaller meals can be beneficial. Including fiber-rich foods alongside proteins and healthy fats within these meals may alleviate discomfort by decelerating digestion rates—incorporation of thickening agents such as guar gum or pectin into one’s diet might also assist digestive processes for some individuals.
For individuals with dumping syndrome, ongoing self-assessment combined with tailored nutrition plans improves living standards significantly. Detecting specific triggers unique to an individual and adjusting their meal plan accordingly plays a key role in managing episodes while ensuring that nutritional needs are met adequately.
Read more: Meal Planning and Cooking for Bariatric Patients
Medical Treatments for Severe Cases
In instances where modifications to diet and lifestyle do not lead to improvement in severe cases, medical treatment may be required. To better control symptoms, doctors can prescribe medications that release slowly into the body. In exceptional circumstances, more aggressive interventions like tube feeding or surgeries for correction might be recommended.
Should these less invasive treatments fail to alleviate discomfort, surgical alternatives such as reversing the gastric bypass surgery may be considered. These surgical measures are usually only contemplated after all other options have been exhausted, emphasizing the critical nature of thorough management approaches.
Complications and Prevention

While dumping syndrome is generally not life-threatening, it can lead to complications if not properly managed. Some potential issues include:
- Rapid Weight Loss and Nutritional Deficiencies: The swift movement of food through the digestive system can prevent proper nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies.
- Persistent Diarrhea: This can result in dehydration, which is particularly concerning for individuals with dumping syndrome.
- Low Blood Sugar: Symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, and faintness can occur due to rapid changes in blood sugar levels.
- Digestive and Kidney Diseases: These conditions can be exacerbated by the symptoms of dumping syndrome.
To prevent these complications, it’s essential to manage dumping syndrome through dietary changes and lifestyle modifications. Here are some strategies:
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: This helps to prevent overwhelming the digestive system and reduces the risk of symptoms.
- Avoid Trigger Foods and Drinks: Identifying and steering clear of foods that cause symptoms is crucial.
- Drink Liquids at the Right Time: Consuming fluids 30 minutes before or after meals can help manage symptoms.
- Take Medications as Prescribed: Follow your doctor’s advice regarding any medications to help control symptoms.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and hygiene practices can prevent infections and dehydration.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can effectively manage dumping syndrome and reduce the risk of complications.
Long-term Management and Lifestyle Changes
Effective long-term control of dumping syndrome necessitates dietary modifications, adjustments to one’s way of life, and ongoing medical assistance. Following bariatric surgery, it’s important for patients to hydrate adequately by drinking at least 64 ounces of fluids each day to circumvent dehydration risks. To prevent muscle degradation while preserving strength, a daily consumption ranging from 60 to 100 grams of protein is advocated.
It is crucial for individuals who have undergone surgery to consistently take supplements that include multivitamins along with particular nutrients such as Vitamin B12 and Calcium in order not just to ward off deficiencies but also to bolster general well-being. Initiating physical activity with gentle exercises like walking can be beneficial in sustaining weight loss and enhancing cardiac fitness. It might become possible for patients post-surgery to lessen or altogether discontinue some medications. Any alterations should invariably occur under strict medical supervision.
Additional behavioral changes are significant for optimal recovery and maintained health well-being surgery. These include quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption. Women are encouraged not only to postpone pregnancy until their weight and nutritional status have stabilized over a period spanning between twelve months and eighteen months following the operation but also to ensure they engage in regular consultations with a specialist in bariatrics so as to track progress meticulously while addressing any persistent health concerns systematically.
Summary
Managing dumping syndrome after gastric sleeve surgery effectively involves a comprehensive approach that includes making dietary adjustments, adopting lifestyle changes, and pursuing medical treatments when necessary. By understanding the causes and symptoms, patients can better anticipate and manage their condition, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Get in Touch with Us
Wellstar Comprehensive Bariatric Services provides an array of resources and expert advice to support patients throughout their post-surgery journey. Our committed team offers personalized care and assistance, ensuring that every individual has the tools needed to successfully navigate their recovery.
Consider reaching out to one of our gastric sleeve surgeons in East Cobb, Marietta, Austell, Smyrna, LaGrange, and other locations across Georgia. Our experts will assist you in creating a tailored treatment plan that meets your specific needs and goals. We understand the challenges of the weight loss journey and are dedicated to helping you achieve long-term success. Contact us today to discover how we can transform your weight loss journey and elevate your health!
