The Duodenal Switch (DS)
As a combination of restrictive and malabsorptive techniques, biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS) represents one of the most effective forms of duo switch surgery in Cobb County for achieving substantial weight loss and addressing obesity-related health issues.
Meet Your Surgeon

Dr. Jean-Pierre
After his general surgery training in Chicago, Dr. JP began his fellowship with a concentration in bariatrics at the Morehouse School of Medicine through Atlanta Medical Center. He is a fellow of the American College of Surgeons and the American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgeons.
How It Works
Procedure
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: About 70-80% of the stomach is removed, creating a smaller, tube-shaped stomach (sleeve) that limits food intake.
- Intestinal Bypass: The small intestine is divided, and a portion is bypassed to reduce calorie and nutrient absorption. The remaining part of the small intestine is connected to the stomach sleeve.
Average Surgery Time
The surgery typically takes about 3 to 4 hours. This duration can vary depending on the patient’s specific circumstances and the surgeon’s experience.
How It Works
- Restriction: The smaller stomach limits the amount of food you can eat.
- Malabsorption: Bypassing a portion of the small intestine reduces the absorption of calories and nutrients.
- Hormonal Changes: The surgery alters gut hormones, reducing hunger and improving satiety.
Recovery Period
- Hospital Stay: Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days. This will depend on the patient’s recovery after surgery.
- Full recovery usually takes about 4-6 weeks, during which patients gradually transition from a liquid diet to solid foods using the post-operatively dietary guidelines.
Potential Complications
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Due to the malabsorptive nature of the surgery, patients are at risk for deficiencies in vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, vitamin D, and B12. Lifelong supplementation and regular monitoring are essential.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate absorption of nutrients can lead to protein and fatty acid deficiencies.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Patients may experience frequent bowel movements, diarrhea, and flatulence.
- Leaks: There is a rare risk of leaks from the stomach or intestines, which can lead to serious infections.
- Blood Clots: The risk of blood clots, including pulmonary embolism, is present, especially in the immediate post-operative period.
- Pneumonia: Post-operative pneumonia can occur, particularly if patients have difficulty with deep breathing and coughing after surgery.
Long-Term Considerations
- Weight Loss Expectations: Patients can expect to lose about 75% to 85% of their excess body weight within three years. This weight loss is typically maintained long-term, especially with adherence to dietary and lifestyle changes.
- Lifelong Supplementation: Patients must commit to taking vitamins and minerals for life to prevent deficiencies.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Ongoing medical check-ups are necessary to monitor nutritional status and manage any complications.
- Dietary Adherence: Following dietary guidelines is crucial to avoid gastrointestinal issues and ensure adequate nutrient intake.
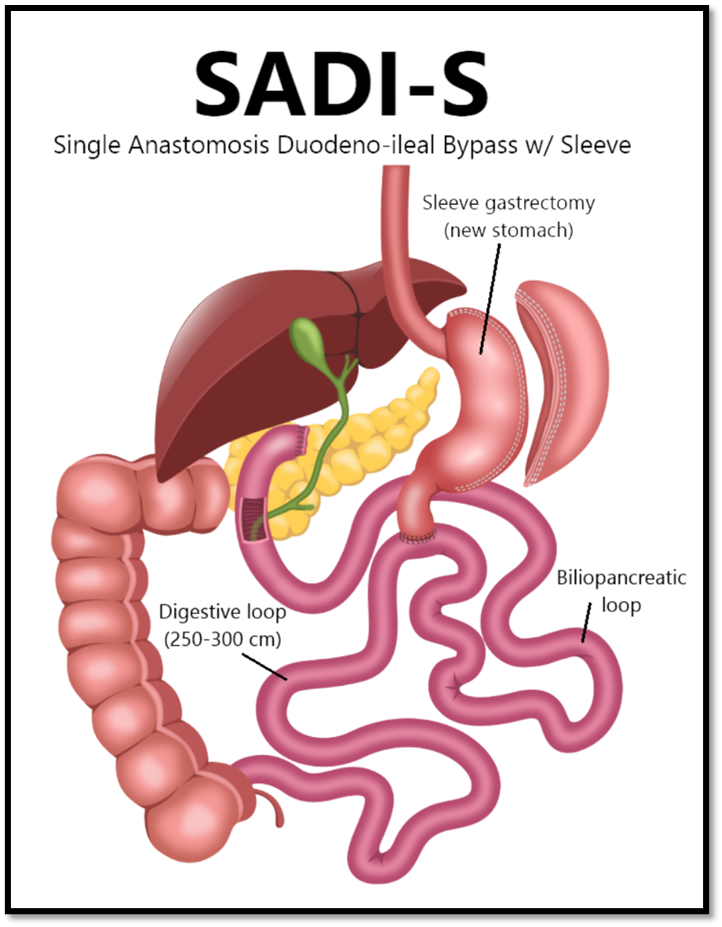
Modified Duodenal Switch also known as Single Anastomosis Duodenal-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy (SADI-S)
The Modified Duodenal Switch, also known as Single Anastomosis Duodenal-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy (SADI-S), is a less invasive version of the traditional duodenal switch. It combines a sleeve gastrectomy with an intestinal bypass but with only one connection (anastomosis) instead of two, which simplifies the procedure and reduces the risk of complications. Here’s a breakdown of how it works and the potential complications:
Procedure
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: About 80% of the stomach is removed, leaving a tube-shaped stomach (sleeve) that restricts food intake.
- Intestinal Bypass: The small intestine is divided just below the stomach, and a loop of the small intestine is connected to the stomach. This bypasses a significant portion of the small intestine, reducing calorie and nutrient absorption.
Average Surgery Time
The surgery typically takes about 2-3 hours. This can vary depending on the patient’s surgical history and anatomy. This duration can vary depending on the complexity of the case and the surgeon’s experience.
How It Works
- Restriction: The smaller stomach limits the amount of food you can eat.
- Malabsorption: Bypassing a portion of the small intestine reduces the absorption of calories and nutrients.
- Hormonal Changes: The altered digestive tract changes levels of gastrointestinal hormones, reducing hunger and increasing feelings of fullness.
Recovery:
- Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 day after the surgery.
- Full recovery usually takes about 4-6 weeks, during which patients gradually transition from a liquid diet to solid foods using the post-operatively dietary guidelines.
Potential Complications
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Due to the malabsorptive nature of the surgery, patients are at risk for deficiencies in vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, vitamin D, and B12. Lifelong supplementation and regular monitoring are essential.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate absorption of nutrients can lead to protein and fatty acid deficiencies.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Patients may experience frequent bowel movements, diarrhea, and flatulence.
- Leaks: There is a rare risk of leaks from the stomach or intestines, which can lead to serious infections.
- Blood Clots: The risk of blood clots, including pulmonary embolism, is present, especially in the immediate postoperative period.
- Pneumonia: Postoperative pneumonia can occur, particularly if patients have difficulty with deep breathing and coughing after surgery.
Long-term Considerations:
Weight Loss Expectations: Patients who undergo modified duodenal switch/SADI surgery typically 70% to 80% of their excess body weight within three years. This weight loss is typically maintained long-term, especially with adherence to dietary and lifestyle changes.
Contact UsFAQs About Duodenal Switch Surgery

Benefits of Duodenal Switch Surgery in Marietta, GA
Sometimes called a bilio-pancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS), this procedure goes beyond a normal gastric sleeve procedure. Like a gastric sleeve, this procedure eliminates most of the stomach and forms it into the shape of a banana. Unlike a gastric sleeve, a duodenal switch also means that the lower intestine is divided. Roughly two-thirds of the intestine is operated on so that food and enzymes cannot be absorbed fully.
Wellstar provides expert bariatric surgeries, including duodenal switch surgery, which can result in dramatic weight loss for the patient. By combining features of gastric bypass with those of duodenal switch surgery, digestion and absorption of nutrients along the gastrointestinal tract are enhanced. Duodenal switch surgery will help mitigate significant problems related to obesity, including diabetes, hypertension, and coronary artery disease. Our team at Wellstar takes pride in personalizing your needs so that together, we can achieve the best results for long-term health benefits.
The benefits of the duodenal switch surgery include substantial and sustainable weight loss. Through this procedure, for many patients, diabetes becomes better controlled, with an overall decrease in medication usage since blood sugar levels are brought under control. Also, cholesterol levels improve, reducing the risk of cardiovascular problems. Compared to other forms of bariatric surgery, this operation produces better long-term outcomes, hence emerging as a good option for morbid obesity.
Why Choose Wellstar for Duodenal Switch Surgery?
At Wellstar, our skilled and experienced duodenal switch surgeons provide quality care and treatment for individuals wanting to lose weight. The duodenal switch surgery is an intricate surgical operation that requires years of experience and expertise from the performing surgeon. At Wellstar, we believe that long-term success can only be achieved using state-of-the-art surgical techniques and comprehensive pre-and post-operative care for each patient. Our dedicated team is passionate about working with you for effective weight loss that reflects an enhanced quality of life by resolving diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleeping disorders.
Our duodenal switch surgeons are highly trained and compassionate professionals who walk you through each step of the process. From initial consultations to follow-up visits, we tailor our attention to your needs and goals. Wellstar helps foster a welcoming environment that supports patient education and well-being. We guarantee the highest level of care with outstanding results, so you’re choosing a trusted healthcare partner to walk through this life-enhancing journey of losing weight with you.
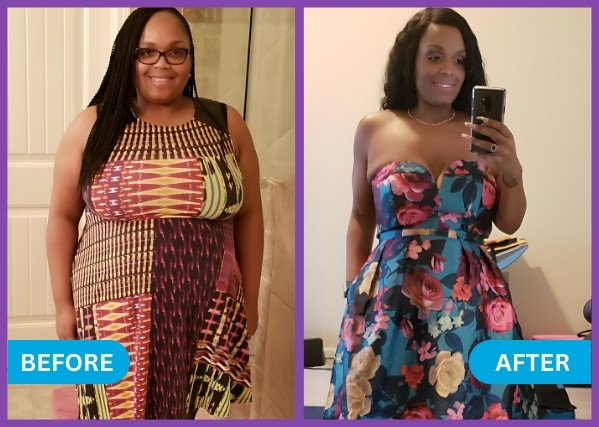
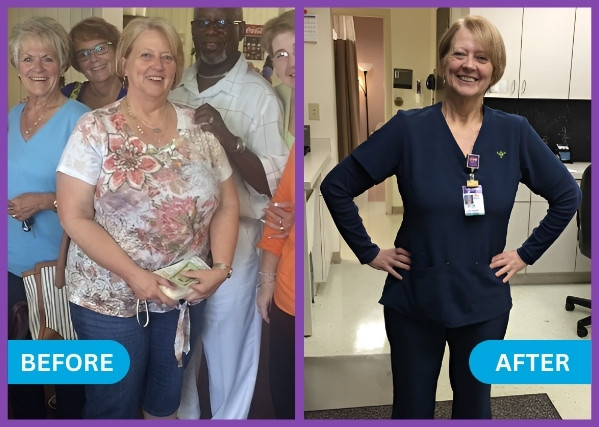
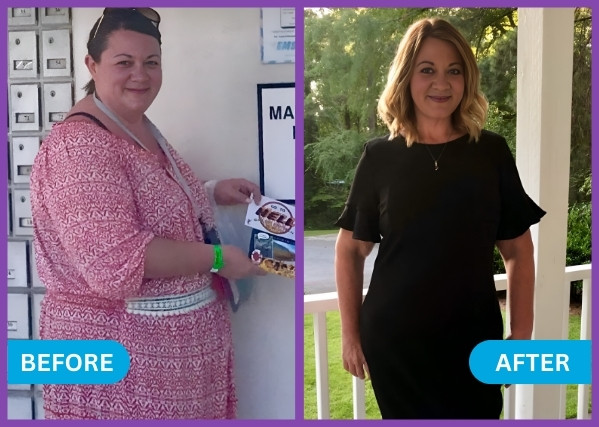
Patient Success Stories
START YOUR TRANSFORMATION TODAY!
Start your journey to lasting weight loss today! Book a Consultation to learn about Gastric Bypass Surgery and how we can support your goals.
Contact UsOur program makes sure you are successful
-

Nutrition and Exercise Support
-

Pre and Post Surgical Support
BMI Calculator
Federal Guidelines for Healthy Weight
- Underweight. Your BMI is less than 18.5.
- Ideal Weight for Your Height. Your BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9.
- Overweight. Your BMI is between 25 and 29.9.
- Obese. Your BMI is 30 or greater.
Blogs
Understanding Your Options: Lipo vs Gastric Bypass
Body contouring and weight loss procedures are often discussed together, but they serve very differ
Read More
Ways to Stop Nausea After Gastric Sleeve
If you’re experiencing nausea after your gastric sleeve procedure, you’re not alone—and there
Read More
How to Choose the Right Hiatal Hernia Surgeon in Marietta
Living with a hiatal hernia can affect more than just your digestion — it can influence your comf
Read More