When it comes to understanding what bariatric surgery method is right for you, Wellstar can help. Visit the comprehensive guides for gastric sleeve, duodenal switch and gastric sleeve, gastric bypass, and LAP-BAND correction to better understand what is right for you.
Register for a seminar today or schedule a consultation with our experts.
Overview:
What is Bariatric/ Metabolic Surgery?
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight-loss surgery, encompasses a variety of procedures designed to help individuals lose weight by altering the digestive and metabolic system. Bariatric Surgery limits the amount of food you eat, causing the body to stop storing excess calories and start using its fat supply for energy. This will cause changes in the gut hormones which may impact hunger, satisfaction, and blood sugar control. Today most bariatric surgeries are performed using minimally invasive techniques, called laparoscopic surgery. Here’s a brief overview:
Different Bariatric Procedures:
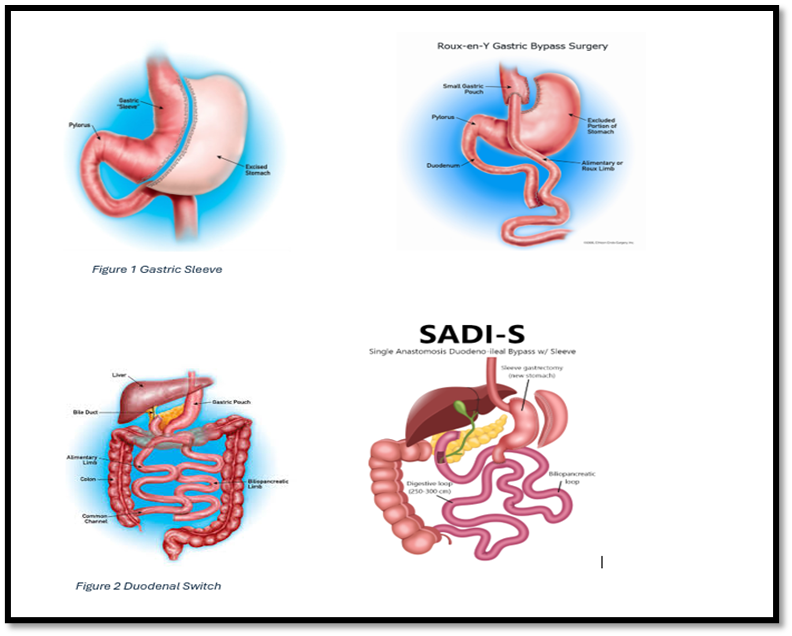
Types of Bariatric Surgery
- Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y): Creates a small stomach pouch and bypasses part of the small intestine, reducing calorie absorption.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: Removes a portion of the stomach, creating a tube-like structure, which limits food intake. (see figure 1)
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): Combines a sleeve gastrectomy with a bypass of a significant portion of the small intestine. (see figure 2)
- Modified Duodenal Switch (SADI-S): It combines a sleeve gastrectomy with an intestinal bypass, but with only one connection (anastomosis) instead of two, which simplifies the procedure and reduces the risk of complications.
- Revision Bariatric Surgery: Surgeries performed to correct complications of previous surgery or covert one type of surgery to another.
Benefits
- Significant weight loss
- Improvement or resolution of obesity-related conditions (e.g., type 2 diabetes, Sleep Apnea, hypertension, and high cholesterol)
- Enhanced quality of life and mobility for patients potentially for years.
Risks
- Surgical complications (e.g., infection, bleeding)
- Nutrient deficiencies.
- Gastrointestinal issues (e.g., dumping syndrome, bowel obstruction)
Requirements
- Typically recommended for individuals with a BMI (Body Mass Index) of more than 40 without any other health conditions
- A BMI (Body Mass Index) between 35 and 39.9 and at least one serious condition related to obesity (such as diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), sleep apnea, or limitations on quality of life)
- A BMI (Body Mass Index) between 30 and 34.9 with metabolic syndrome or diabetes that isn’t being controlled with medications.
- Requires a commitment to lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, and regular follow-up care.
Understanding your Surgical Options- Estimates of Bariatric Surgery Benefits
Here’s a summary of the estimated benefits of various bariatric surgeries, including gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, duodenal switch, and modified duodenal switch (SADI-S), focusing on total weight loss after three years, resolution of type 2 diabetes, resolution of hypertension, improvement in high cholesterol, and resolution of sleep apnea:
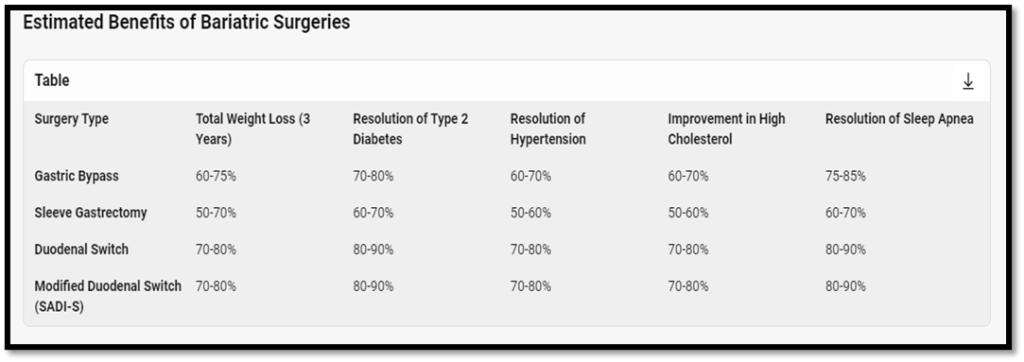
Key Points
- Total Weight Loss: The duodenal switch and modified duodenal switch (SADI-S) generally result in the highest percentage of excess weight loss, followed by gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy.
- Resolution of Type 2 Diabetes: Both the duodenal switch and SADI-S show the highest rates of diabetes resolution, with gastric bypass also showing significant improvement.
- Resolution of Hypertension: Similar trends are seen with hypertension, where the duodenal switch and SADI-S have the highest resolution rates.
- Improvement in High Cholesterol: All procedures show substantial improvement, with the duodenal switch and SADI-S leading.
- Resolution of Sleep Apnea: The duodenal switch and SADI-S again show the highest rates of resolution, followed by gastric bypass.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: High rate of GERD improvement has been observed following Gastric Bypass/RNY with some studies citing over 70% remission of symptoms.
These estimates can vary based on individual health conditions, adherence to post-surgery guidelines, and lifestyle changes. It’s always best to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable procedure for your specific needs.
