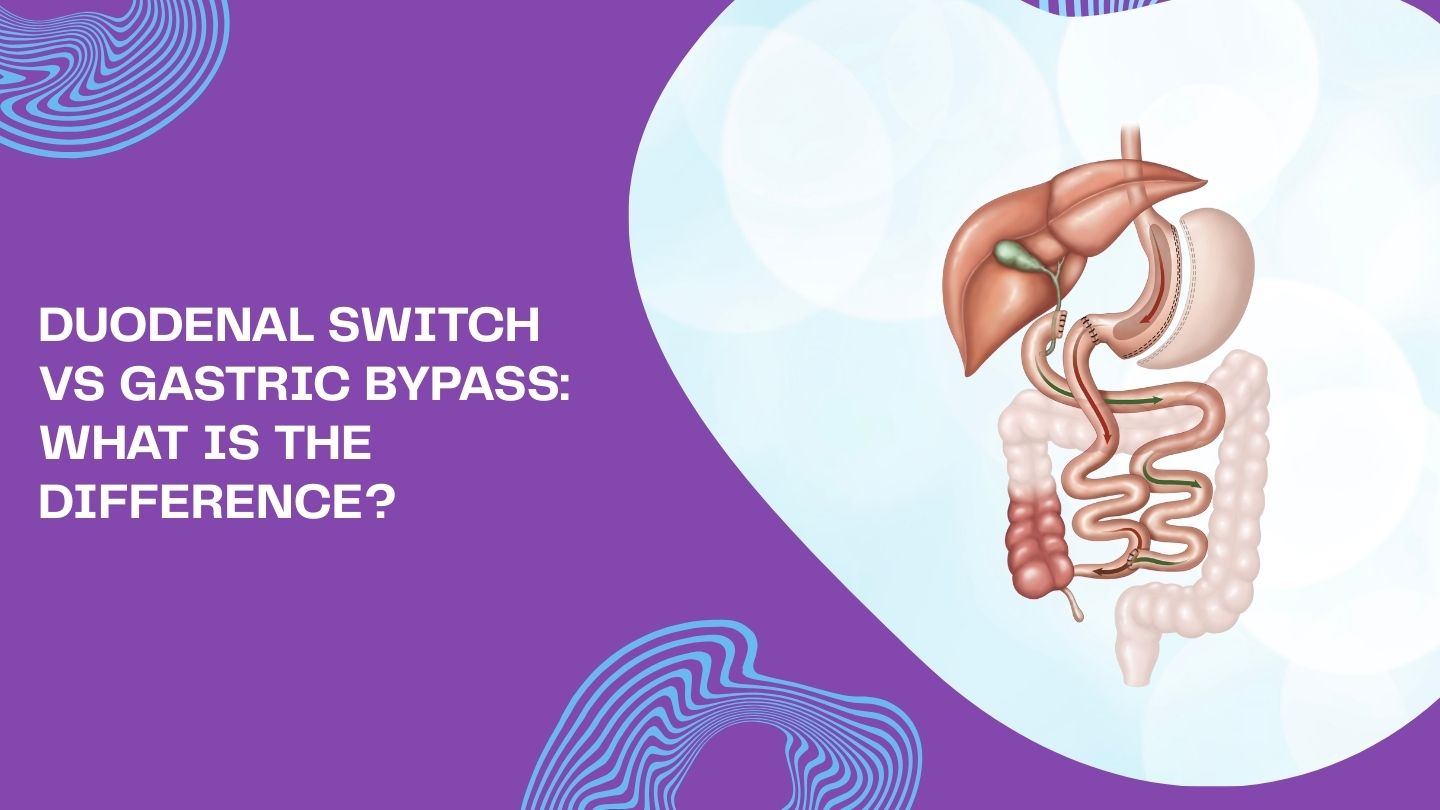
Duodenal Switch vs Gastric Bypass: What Is the Difference?
When you’re exploring weight loss surgery options, understanding the differences between procedures can feel overwhelming. Both the duodenal switch and gastric bypass are powerful tools for achieving significant weight loss and improving obesity-related health conditions, but they work in different ways and suit different needs.
At their core, both are bariatric procedures that reduce stomach size and reroute part of the small intestine. However, the extent of these changes, the typical candidates, and the long-term lifestyle requirements vary considerably between the two. Whether you’re just beginning to research your options or preparing for a consultation with an experienced bariatric surgeon, this blog will help you understand what sets these surgical procedures apart and which might align with your health goals.
Key Takeaways
- Duodenal switch typically produces more weight loss (75–85% of excess weight) compared to gastric bypass (60–70%), making it especially effective for patients with very high BMI
- Both surgeries improve type 2 diabetes and metabolic conditions, but the duodenal switch often shows higher remission rates for diabetes and high cholesterol due to more extensive malabsorption
- Gastric bypass is more widely performed and slightly less complex, often recommended for patients with a BMI of 40–50 or those with significant acid reflux (GERD)
- Duodenal switch carries a higher risk of nutritional deficiencies and requires stricter lifelong supplement regimens and more frequent follow-up bloodwork
- The right choice depends on your individual situation, including your body mass index, existing health conditions, tolerance for dietary restrictions, and guidance from your healthcare provider
Duodenal Switch vs Gastric Bypass: Quick Comparison
Before diving into the details, here’s an at-a-glance look at comparing duodenal switch and gastric bypass so you can quickly grasp the main distinctions between these two procedures.
Type of Surgery:
- Duodenal switch (BPD-DS): Combines vertical sleeve gastrectomy with extensive intestinal rerouting
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: Creates a small stomach pouch connected directly to the mid-small intestine
Typical BMI Range:
- Duodenal switch: Often recommended for BMI ≥50 (super-obese patients)
- Gastric bypass: Commonly performed for BMI ≥40, or ≥35 with obesity-related conditions
Average Excess Weight Loss:
- Duodenal switch: Approximately 75–85% (sometimes higher)
- Gastric bypass: Approximately 60–70%
Impact on Health Conditions:
- Both significantly improve type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol
- Duodenal switch shows especially strong effects on insulin resistance and lipid levels
Intestinal Bypass Extent:
- Duodenal switch bypasses a significant portion of the small intestine, roughly 75%, dramatically limiting calorie absorption and fat absorption
- Gastric bypass bypasses approximately 30–60% of the small intestine, creating more balanced restriction and reduced calorie absorption
Lifestyle Implications:
- Duodenal switch requires a stricter lifelong vitamin and mineral supplements regimen with closer follow-up monitoring
- Gastric bypass still requires daily supplements, but typically with a lower risk of severe malabsorption complications
Both are major surgeries typically performed laparoscopically by fellowship-trained bariatric surgeons. The surgeon’s experience with each procedure matters as much as the procedure choice itself.
What Is Gastric Bypass Surgery (Roux-en-Y)?
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass has been the most widely performed bariatric surgery in the United States and globally for the past two decades. Its long track record and consistent effectiveness make it what many consider the “gold standard” in metabolic and bariatric surgery.
How the Gastric Bypass Procedure Works:
During the gastric bypass procedure, your bariatric surgeon creates a very small stomach pouch, about the size of an egg or golf ball, holding roughly 1–2 ounces. This new stomach pouch is separated from the rest of your stomach and connected directly to a loop of small intestine called the “Roux limb.” Food bypasses the larger portion of your stomach and the first portion of your small intestine entirely.
Restriction Mechanism:
The tiny pouch fills quickly, so patients feel full after just a few small bites. This dramatically reduces food intake and changes hunger hormones. The body’s ability to produce ghrelin (the “hunger hormone”) decreases, while hormones like GLP-1 that promote fullness increase. Most patients find they naturally eat less food without feeling deprived.
Read More: Everything You Need to Know About Hunger Gastric Bypass Recovery
Malabsorption Component:
Because food skips the duodenum and a portion of the jejunum, fewer calories and nutrients are absorbed into your body. The length of the bypassed segment can vary depending on your surgeon’s technique and your individual needs. This reduced calorie absorption contributes to weight loss beyond what restriction alone would achieve.
Typical Candidates for Gastric Bypass:
- Body mass index ≥40
- BMI ≥35 with obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, or severe GERD
- Patients who have not achieved adequate weight loss expectations through lifestyle changes alone
- Those with significant reflux disease, as gastric bypass often improves GERD symptoms
Expected Outcomes:
Average excess weight loss typically reaches 60–70% within 12–18 months. Many patients see rapid improvement, or complete remission, of type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure within weeks to months after surgery. Long-term studies show sustained benefits for the right patients who maintain healthy lifestyle habits.
Important Considerations:
Patients should be aware of potential complications related to gastric bypass, including dumping syndrome, marginal ulcers, and the possibility of future revisional needs, questions that sometimes arise around scenarios like can you get gastric bypass twice in long-term bariatric care planning. Regular lab monitoring per your bariatric program’s protocol helps catch and address any nutritional deficiencies early.
Read More: A Comprehensive Guide to Gastric Bypass Surgery
What Is Duodenal Switch Surgery (Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch)?
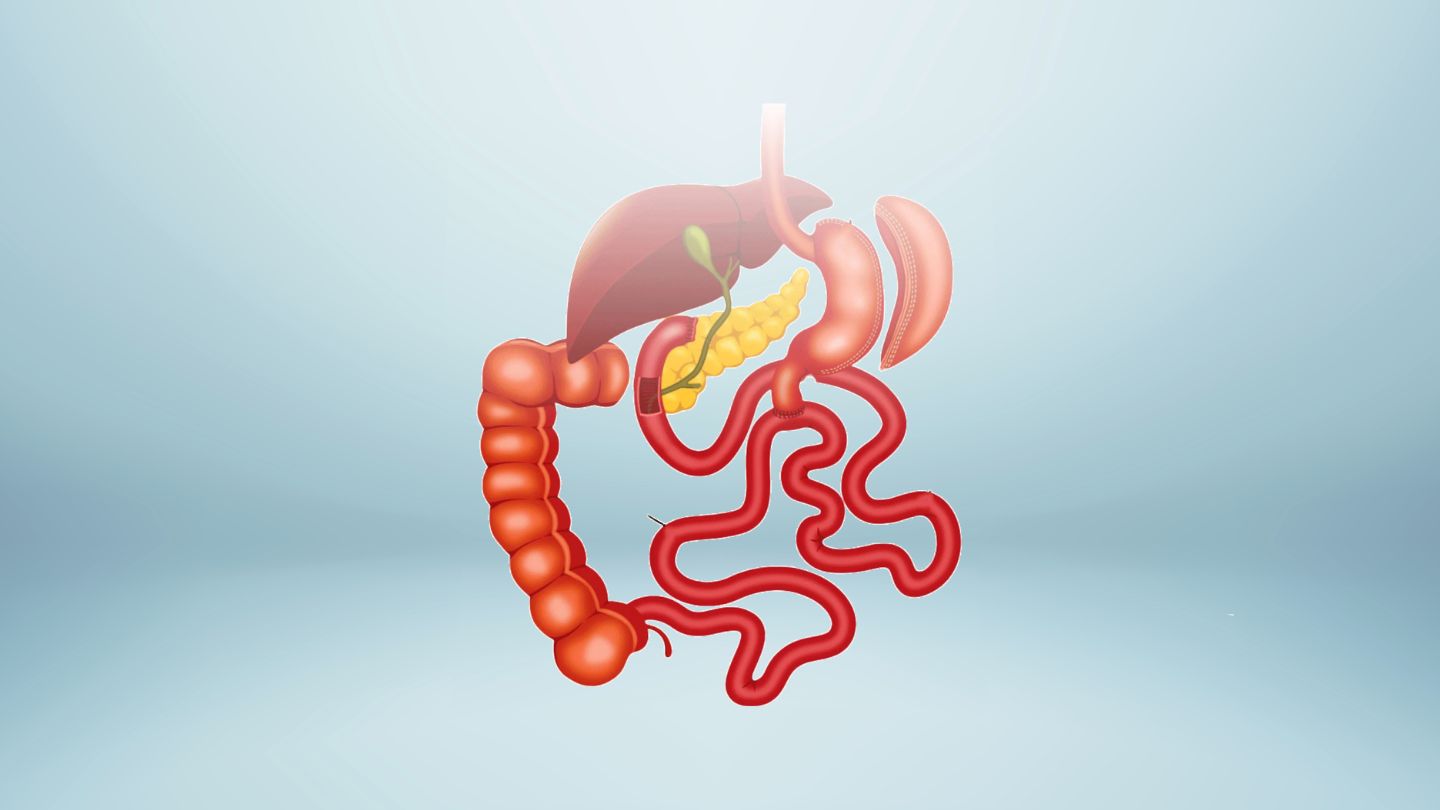
The duodenal switch, formally known as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS), is a two-part bariatric surgery that combines a sleeve gastrectomy with significant rerouting of the digestive system. This procedure maximizes both weight loss and metabolic effects, making it particularly powerful for patients with very high BMI.
The Sleeve Component:
During duodenal switch surgery, your surgeon first performs a vertical sleeve gastrectomy, removing roughly two-thirds to 80% of the outer curved portion of your stomach. This leaves a narrow, banana-shaped “sleeve” with a typical capacity of about 3–5 ounces, larger than a gastric bypass pouch but still dramatically smaller than the original stomach. Importantly, the pylorus (the natural valve between the stomach and the intestine) is preserved, allowing patients to maintain more normal stomach function.
The Intestinal Rerouting:
After creating the sleeve, the surgeon divides the duodenum just beyond the pylorus. The lower portion of the small intestine is then connected to this divided area, creating a new pathway for food. Digestive juices (bile and pancreatic enzymes) travel through a separate pathway and mix with food only in a short “common channel” near the end of the small intestine. This dramatically limits the digestive process and how many calories your body can absorb.
Strongly Malabsorptive Nature:
Duodenal switch bypasses a significant portion of the small intestine, often 60–75%. This substantially reduces absorption of fats and calories, leading to greater weight loss than less malabsorptive procedures. However, this also means a higher risk of nutritional deficiencies if supplement protocols aren’t strictly followed.
Typical Candidates for Duodenal Switch:
- Patients with very high BMI (often ≥50)
- Those with severe or long-standing type 2 diabetes that has been difficult to control
- Individuals with significantly high cholesterol or triglyceride issues
- Patients who have had a previous gastric sleeve procedure but haven’t achieved adequate weight loss
Expected Outcomes:
Average excess weight loss with duodenal switch reaches 75–85%, with some patients achieving even higher results. This procedure shows excellent rates of diabetes remission, approximately 90%, along with strong improvement in cholesterol and triglyceride levels over several years. For super-obese patients, research indicates that the duodenal switch often maintains weight loss better over 5–10 years compared to other procedures.
Risks and Lifestyle Requirements:
Patients considering duodenal switch should understand the trade-offs. Frequent or oily stools, gas, and foul-smelling bowel movements are more common with this procedure. There’s a higher risk of protein malnutrition and deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), iron, and calcium. Success requires strict adherence to a high-protein, healthy diet, prescribed vitamin regimen, and regular follow-up bloodwork for life, which closely aligns with established guidance for diet after duodenal switch surgery.
Read More: Duodenal Switch Surgery Advantages and Requirements
Duodenal Switch vs Gastric Bypass: Key Differences
While both surgeries reduce stomach size and bypass part of the intestine, they differ significantly in how aggressively they limit absorption, who they’re best suited for, and what long-term challenges patients may face. Understanding these differences helps you prepare for an informed conversation with your bariatric team. Bowel habit changes are more pronounced after duodenal switch, with frequent or oily stools, gas, and foul-smelling bowel movements reflecting well-documented common digestive issues after the duodenal switch that require long-term dietary awareness and adherence.
Surgical Complexity:
Duodenal switch is generally a longer, more complex operation than gastric bypass. It’s performed by a smaller subset of bariatric surgeons who have specialized training and experience with this specific procedure. Not all bariatric centers offer duodenal switch, which can affect availability depending on where you live.
Stomach Size and Function:
| Feature | Gastric Bypass | Duodenal Switch |
| Pouch/Sleeve Size | ~1–2 ounces | ~3–5 ounces |
| Pylorus Preserved | No | Yes |
| Stomach Tissue Removed | Bypassed but not removed | Two-thirds or more removed |
| Eating Experience | Very small portions | Small but more “normal-feeling” portions |
The gastric bypass pouch is smaller and completely disconnected from most of the original stomach. The duodenal switch leaves a larger tubular stomach that maintains the natural pylorus, allowing patients to experience more normal stomach emptying and reducing the risk of dumping syndrome.
Intestinal Bypass Extent:
Duodenal switch vs gastric bypass differs most dramatically in how much small intestine is bypassed. Standard Roux-en-Y typically bypasses 100–200 cm of jejunum (roughly 30–60% of the small intestine), while duodenal switch bypasses approximately 75% of intestinal length. This difference in limiting calorie absorption accounts for much of the variation in weight loss outcomes.
Weight Loss Expectations:
Switch vs gastric bypass comparisons consistently show:
- Duodenal switch: 75–85% excess weight loss (approximately 40% total body weight loss)
- Gastric bypass: 60–70% excess weight loss (approximately 29–34% total body weight loss)
Research on super-obese patients (average starting weight around 368 lbs) found that those who underwent duodenal switch lost an average of 173 pounds at 3 years, compared to 118 pounds for gastric bypass patients. Duodenal switch also tends to maintain weight loss better in the 5–10 year timeframe, especially for those with very high starting BMI.
Metabolic Impact:
Both procedures significantly improve diabetes and metabolic syndrome. However, the duodenal switch tends to have especially powerful effects on insulin resistance and lipid levels. The profound malabsorption of fats contributes to a significant decrease in cholesterol and triglycerides that often exceeds what gastric bypass achieves.
Availability and Surgeon Preference:
Gastric bypass is more widely offered at bariatric centers and is often the “default” recommendation for patients meeting surgical criteria. Duodenal switch may be suggested specifically for revisional surgery after inadequate weight loss from sleeve gastrectomy, particularly in complex bariatric histories where questions similar to can you get gastric bypass twice become part of the surgical decision-making process.
- Very high BMI cases (≥50)
- Revisional surgery after inadequate weight loss from sleeve gastrectomy
- Patients with severe metabolic conditions, when centers have the necessary expertise
Outcomes: Weight Loss, Health Benefits, and Long-Term Results

Both duodenal switch and gastric bypass can produce life-changing results. Understanding typical outcomes helps set realistic weight loss goals while recognizing that individual results vary based on many factors.
Gastric Bypass Weight Loss Trajectory:
- Rapid weight loss during the first 6–12 months
- Weight typically stabilizes around 18–24 months post-surgery
- Most patients lose 60–70% of excess body weight
- Some weight regain is common (10–15 lbs from the lowest point is typical)
- Long-term maintenance is significantly better than lifestyle changes alone
Duodenal Switch Weight Loss Trajectory:
- Greater average excess weight loss: 75–85%
- Stronger long-term weight maintenance, especially in very high BMI patients
- Super-obese patients show particularly impressive results (average 173 lbs lost at 3 years in research studies)
- Lower rates of significant weight regain at 5–10 years
- Approximately 40% total body weight loss for most patients
Resolution of Obesity-Related Conditions:
| Condition | Gastric Bypass | Duodenal Switch |
| Type 2 Diabetes | 60–70% remission | ~90% remission |
| High Blood Pressure | Significant improvement | Significant improvement |
| High Cholesterol | Improved | Often dramatically improved |
| Sleep Apnea | Often resolved | Often resolved |
| Joint Pain | Improved with weight loss | Improved with weight loss |
| Heart Disease Risk | Reduced | Reduced |
Quality of Life Improvements:
Beyond the numbers, patients commonly report:
- Improved mobility and ability to participate in activities previously difficult
- Increased energy and stamina
- Better sleep quality
- Improved fertility for some patients
- Greater confidence and psychological well-being
- Reduced need for medications
The Role of Patient Commitment:
“Success” with either procedure requires ongoing effort. Surgery provides a powerful tool, but not a stand-alone cure for obesity. Patients who achieve the best long-term outcomes:
- Follow dietary guidelines consistently
- Engage in regular exercise as part of a healthy lifestyle
- Attend scheduled follow-up visits
- Take prescribed supplements faithfully
- Seek psychological support when needed
Recovery and Long-Term Lifestyle After Surgery
Recovery timelines are similar for gastric bypass and duodenal switch when performed laparoscopically. However, the long-term lifestyle adjustments differ somewhat based on each procedure’s unique characteristics.
Immediate Recovery:
- Average hospital stay: 1–3 days for uncomplicated laparoscopic cases
- Most patients return to non-strenuous work in 2–4 weeks
- Driving typically resumes within 1–2 weeks (when no longer taking narcotic pain medication)
- Full recovery: 4–6 weeks
Early Diet Progression:
| Phase | Duration | What’s Allowed |
| Clear Liquids | Days 1–7 | Water, broth, sugar-free gelatin |
| Full Liquids | Weeks 1–2 | Protein shakes, thin soups, milk |
| Puréed Foods | Weeks 2–4 | Blended proteins, soft foods |
| Soft Foods | Weeks 4–6 | Scrambled eggs, soft fish, cooked vegetables |
| Regular Diet | Week 6+ | Small portions of most foods, protein first |
Specific timelines vary by program, so follow your bariatric team’s guidelines.
Activity Recommendations:
- Light walking: Start as soon as possible after surgery to reduce blood clot risk
- Heavy lifting: Avoid for approximately 4–6 weeks
- Strenuous exercise: Gradually reintroduce as cleared by your surgical team
- Goal: Build toward 150+ minutes of moderate activity weekly
Regular exercise becomes essential for maintaining weight loss and building lean muscle mass as you lose weight.
Long-Term Eating Habits:
Allowing patients to lose weight and keep it off requires permanent dietary changes:
- Multiple small meals daily (5–6 instead of 3 large meals)
- Protein first at every meal (lean meats, eggs, dairy, legumes)
- Careful chewing (20–30 times per bite)
- Avoid drinking with meals (wait 30 minutes after eating)
- Limit high-sugar and high-fat foods to prevent dumping (bypass) or oily stools (DS)
- Stay well-hydrated between meals (64+ ounces daily)
- Stop eating when satisfied, not full
The Importance of Support Systems:
Long-term success isn’t just about food and exercise. Patients who thrive often:
- Participate in bariatric support groups (in-person or online)
- Maintain regular visits with their bariatric dietitian
- Seek mental health support for body-image adjustments and emotional eating patterns
- Connect with others who have had similar procedures
- Build accountability partnerships
Your healthcare provider can connect you with resources that support your ongoing journey toward a healthy weight.
How to Choose Between Duodenal Switch and Gastric Bypass
No single procedure is “best” for everyone. The right choice emerges from honest self-reflection, thorough medical evaluation, and collaborative discussion with your bariatric team.
Key Questions to Consider:
- What is my current BMI? (Higher BMI often favors duodenal switch)
- Do I have severe diabetes or high cholesterol that has been difficult to control?
- Do I have significant GERD/acid reflux? (May favor gastric bypass)
- Have I had a previous bariatric surgery?
- How willing am I to take supplements multiple times daily for life?
- Can I commit to regular follow-up appointments and bloodwork?
When Duodenal Switch May Be Recommended:
Patients with extreme obesity (BMI ≥50) or very difficult-to-control diabetes may benefit most from the stronger metabolic effects of duodenal switch. If you’ve already had a gastric sleeve procedure with inadequate weight loss, the duodenal switch is often the natural next step.
When Gastric Bypass May Be Recommended:
Patients with moderate to severe GERD, or those seeking a time-tested procedure with a more balanced approach to restriction and malabsorption, may be better served by gastric bypass. It’s also more widely available and may be preferred when duodenal switch expertise isn’t locally accessible.
Evaluating Surgeon and Center Experience:
Important questions to ask:
- How many duodenal switch procedures does your center perform annually?
- How many gastric bypass procedures?
- What are your complication rates for each?
- What long-term follow-up and nutritional support do you provide?
- Will I have access to dietitians, behavioral health specialists, and support groups?
Insurance and Practical Considerations:
Not all insurance plans cover duodenal switch, and not all hospitals offer it. These practical realities can influence choices even when a particular procedure is clinically appropriate. Your bariatric coordinator can help navigate insurance requirements and coverage.
Preparing for Your Consultation:
- Bring a written list of questions
- Attend an information seminar or class if offered by your bariatric program
- Be honest about your eating habits, activity level, and support system
- Ask about outcomes for patients similar to you
- Don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion if uncertain
Making the Right Choice for Long-Term Success
Choosing between duodenal switch and gastric bypass depends on your health history, weight loss goals, and ability to manage long-term nutritional needs. Both procedures are effective but differ in complexity, risks, and lifestyle impact. Understanding these differences helps patients make informed, confident decisions that support sustainable weight loss and overall health.
At Wellstar Comprehensive Bariatric Services, we focus on personalized care plans such as gastric bypass in Cobb County, Marietta, Smyrna, Austell, LaGrange, and West GA that align with your medical needs and long-term success. Whether you’re considering gastric sleeve, duodenal switch with gastric sleeve, revisional bariatric surgery, or managing GERD, our expert guidance is here to help. If you’re ready to explore your options, connect with us to take the next step toward lasting weight management and improved well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can either procedure be reversed or revised?
Both gastric bypass and duodenal switch are intended as permanent surgeries. Gastric bypass can sometimes be revised for complications or weight regain, though reversal is rare and risky. Duodenal switch may be modified by adjusting the common channel, but full reversal is highly complex and uncommon.
Which surgery is better if I already have a gastric sleeve?
If weight loss after a sleeve is inadequate, the duodenal switch is often used as a second-stage procedure by adding an intestinal bypass. However, if severe reflux is the primary issue, conversion to gastric bypass is usually preferred because it more reliably improves GERD symptoms.
Will I have significant bowel habit changes?
Bowel changes are typically more pronounced after duodenal switch, including frequent, oily, or foul-smelling stools due to fat malabsorption. Gastric bypass patients usually experience bowel changes related to specific foods, such as diarrhea after high-sugar intake, rather than persistent stool changes.
Can I get pregnant after bariatric surgery?
Most experts recommend waiting 12–18 months after surgery before pregnancy to allow weight and nutrition to stabilize. Pregnancy after duodenal switch requires especially close monitoring due to higher malabsorption risks, making coordinated care with your bariatric team and obstetrician essential.